How to use zookeeper commands? After preparing the corresponding configuration, you can directly use the zkServer.sh script to perform service-related operations, such as starting the zookeeper service, viewing the zookeeper service status, stopping the zookeeper service, and restarting the zookeeper service.

1. zkServer.sh
View zkServer.sh help information
[root@bigdata05 bin]# ./zkServer.sh help
ZooKeeper JMX enabled by default
Using config: /bigdata/zookeeper-3.4.10/bin/../conf/zoo.cfg
Usage: ./zkServer.sh {start|start-foreground|stop|restart|status|upgrade|print-cmd}
Start/stop zk server
[root@bigdata05 bin]# ./zkServer.sh start [root@bigdata05 bin]# ./zkServer.sh stop
View server status
[root@bigdata05 bin]# ./zkServer.sh status ZooKeeper JMX enabled by default Using config: /bigdata/zookeeper-3.4.10/bin/../conf/zoo.cfg Mode: follower
2. zkCli.sh
View the help information of zkCli.sh
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 0] help ZooKeeper -server host:port cmd args stat path [watch] set path data [version] ls path [watch] delquota [-n|-b] path ls2 path [watch] setAcl path acl setquota -n|-b val path history redo cmdno printwatches on|off delete path [version] sync path listquota path rmr path get path [watch] create [-s] [-e] path data acl addauth scheme auth quit getAcl path close connect host:port
Common commands
Connect to zookeeper
[root@bigdata05 bin]# ./zkCli.sh -server localhost:2181
View the current node list
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 1] ls / [zookeeper, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha]
Create a node
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 1] ls / [zookeeper, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha] [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 2] create /test "test" Created /test [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 3] ls / [zookeeper, test, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha] [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 4] create /test/test "test" Created /test/test [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 5] ls / [zookeeper, test, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha] [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 6] ls /test [test]
View node data
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 7] get /test test cZxid = 0x400000031 ctime = Mon Oct 16 04:05:02 CST 2017 mZxid = 0x400000031 mtime = Mon Oct 16 04:05:02 CST 2017 pZxid = 0x400000032 cversion = 1 dataVersion = 0 aclVersion = 0 ephemeralOwner = 0x0 dataLength = 4 numChildren = 1
Set node data
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 8] set /test "666666" cZxid = 0x400000031 ctime = Mon Oct 16 04:05:02 CST 2017 mZxid = 0x400000033 mtime = Mon Oct 16 04:08:44 CST 2017 pZxid = 0x400000032 cversion = 1 dataVersion = 1 aclVersion = 0 ephemeralOwner = 0x0 dataLength = 6 numChildren = 1 [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 10] get /test 666666 cZxid = 0x400000031 ctime = Mon Oct 16 04:05:02 CST 2017 mZxid = 0x400000033 mtime = Mon Oct 16 04:08:44 CST 2017 pZxid = 0x400000032 cversion = 1 dataVersion = 1 aclVersion = 0 ephemeralOwner = 0x0 dataLength = 6 numChildren = 1
Delete node
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 11] delete /test Node not empty: /test [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 12] ls / [zookeeper, test, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha] [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 13] delete /test/test [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 14] ls /test [] [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 15] delete /test [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 16] ls / [zookeeper, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha]
3. ZooKeeper server side four character command
ZooKeeper supports some specific four-letter commands (The Four Letter Words) to interact with it. Most of them are query commands to obtain the current status and related information of the ZooKeeper service. Users can submit corresponding commands to ZooKeeper via telnet or nc on the client. ZooKeeper commonly used four-character commands are mainly as follows:
| ZooKeeper four-word commands | Function description |
|---|---|
| conf | Introduced in version 3.3.0. Print out the detailed information of the service-related configuration. |
| cons | Introduced in version 3.3.0. List all the connection/session details of all clients connected to this server. Including the number of “received/sent” packets, session id, operation delay, last operation execution and so on. |
| crst | Introduced in version 3.3.0. Reset connection and session statistics for all connections. |
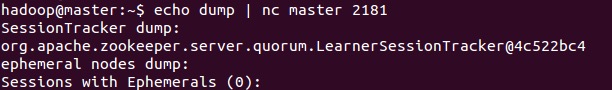
| dump | List the more important sessions and temporary nodes. This command can only be useful on the leader node. |
| envy | Print out the detailed information of the service environment. |
| reqs | List unprocessed requests |
| food | Test whether the service is in the correct state. If it does, then the service returns “imok”, otherwise it does nothing. |
| state | Output a list of performance and connected clients. |
| hair | Reset server statistics. |
| srvr | Introduced in version 3.3.0. List the detailed information of the connected server |
| wchs | Introduced in version 3.3.0. List the detailed information of the server watch. |
| wchc | Introduced in version 3.3.0. List the detailed information of the server watch through the session, and its output is a list of sessions related to the watch. |
| wchp | Introduced in version 3.3.0. List the detailed information of the server watch by path. It outputs a path related to the session. |
| mntr | Introduced in version 3.4.0. Output a list of variables that can be used to detect the health status of the cluster |
##conf conf command was introduced in version 3.3.0, it will print out the detailed information of the server configuration. So that the operation and maintenance personnel can quickly view some configuration parameters of the ZooKeeper server when it is currently running.
telnet example
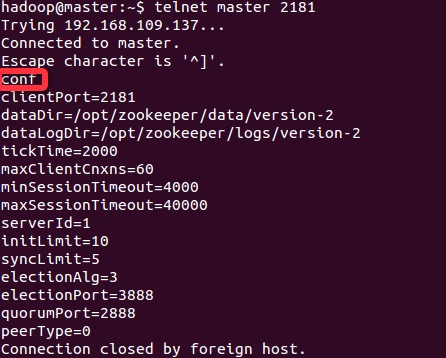
You can see that some configuration items are not configured in the zoo.cfg configuration file, and the server uses the default configuration.
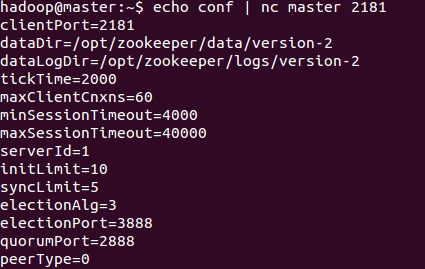
nc example
Operating mode
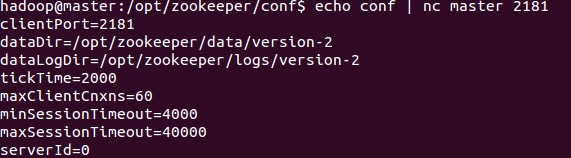
The conf command will determine the server configuration information printed out according to the current operating mode. The above two examples are examples in cluster mode. If it is in standalone mode, it will not output clusters such as initLimit, syncLimit, electionAlg, and electionPort. Configuration information.
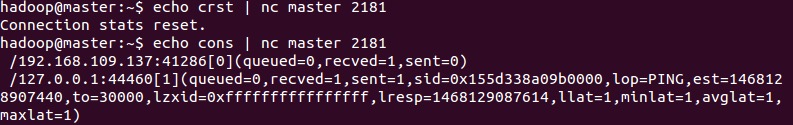
##cons cons command was introduced in version 3.3.0, it is used to output the complete connection and session information of all clients connected to the server, including the number of received and sent packets, session ID, operation delay, and the last operation performed And other information.
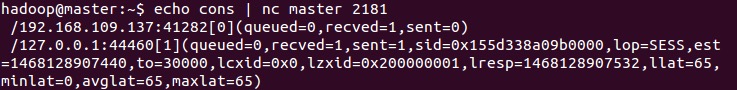
You can see that there is a client connection on this machine.
##crst The crst command was introduced in version 3.3.0 and is used to reset the connection and session statistics of all client connections.
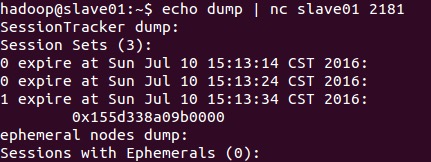
##dump dump command is used to output unfinished sessions and temporary nodes.
###leader example
###follower example
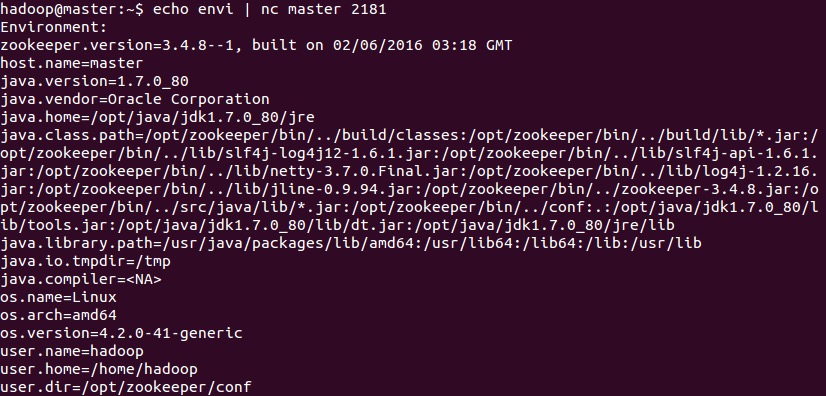
##envi envi command is used to print out the environment variable information when the server is running.
##ruok ruok command is used to test whether the current server is running. If the server is running, it returns “imok”, otherwise there is no response.

It should be noted that the “imok” response does not necessarily indicate that the server has joined the cluster, but only indicates that the server process is active and has been bound to the specified client port. You can use “stat” to get the cluster status and client connection information.
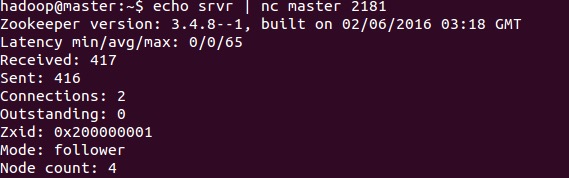
##srst The srst command is used to reset server statistics.
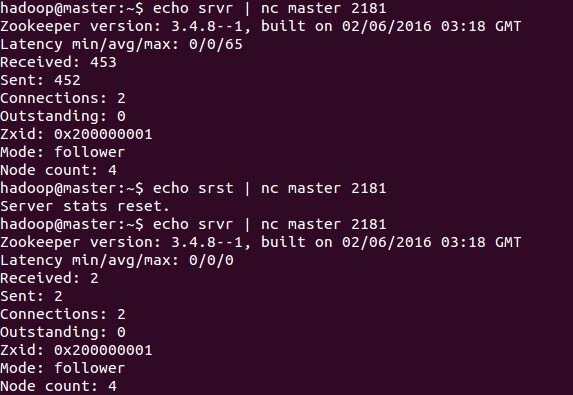
##srvr The srvr command was introduced in version 3.3.0, and it is used to output the complete information of the server.
##stat The stat command is used to output the summary information of the server and the clients connected to the server.
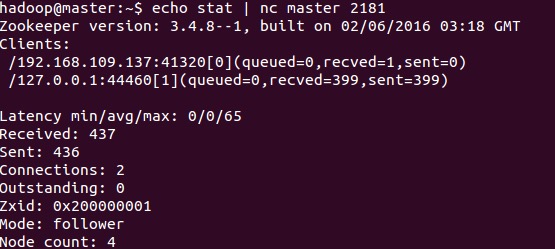
The only difference between the srvr command and the stat command is that srvr does not output the summary information of the client.
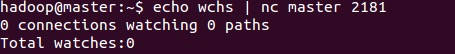
##wchs The wchs command was introduced in version 3.3.0 and is used to output the summary information of Watcher on the current server.
##wchc The wchc command was introduced in version 3.3.0 and is used to output the detailed information of the watches on the current server by session. It will output a list of sessions (connections) and related watches (paths).

Because there are no watches for the time being, there is no output.
Note that depending on the number of watches, this operation may be very time-consuming (affecting server performance), so it needs to be used with caution.
##wchp The wchp command was introduced in version 3.3.0 and is used to output detailed information of watches on the current server by path. It will output the path (znodes) and a list of related sessions.

Similarly, because there are no watches for the time being, there is no output.
Note that depending on the number of watches, this operation may be very time-consuming (affecting server performance), so it needs to be used with caution.
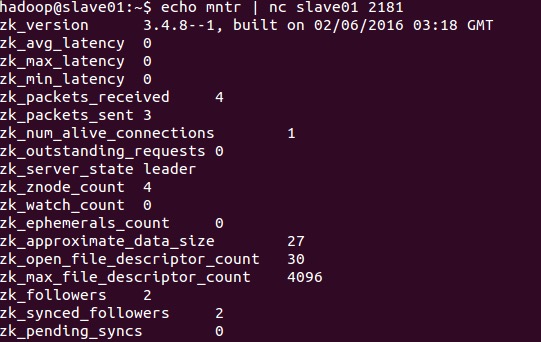
##mntr The mntr command was introduced in version 3.4.0 and is used to output a list of variables that can be used to monitor the health of the cluster.
###leader example
###follower example
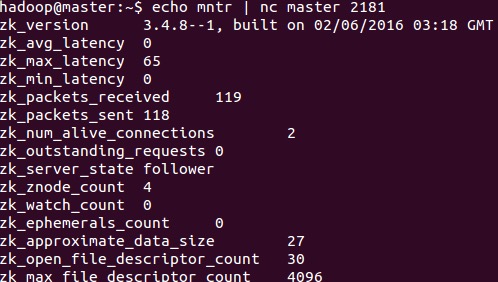
###Example description As can be seen from the above two examples, zk_followers, zk_synced_followers and zk_pending_syncs will only be output when the mntr command is run on the leader server. Also note that the two variables zk_open_file_descriptor_count and zk_max_file_descriptor_count are only available on Unix platforms.



