How to use js postMessage to transfer messages across domains? In daily development work, when we need to send messages across domains on the client side, the postMessage provided by javascript can help us. In this post, I will record a single-minded technique to prevent it from being forgotten later.
postMessage to transfer messages across domains
window.postMessage() Methods can be safely implemented between Window objects cross tranfser message. For example, between a page and the pop-up window it generates, or between the page and the iframe embedded in it.
Under normal circumstances, cross-domain issues are always a problem due to browser “same-origin policy” restrictions, and window.postMessage()a controlled mechanism is provided to safely circumvent this restriction (if used properly).
Grammar
Generally speaking, a window can obtain a reference to another window (for example, through targetWindow=window.opener), and then use targetWindow.postMessage()it to distribute MessageEvent. The receiving window can then handle this event on its own as needed, and the passed window.postMessage()parameters are exposed to the receiving window through the event object.
Basic syntax:
targetWindow.postMessage(message, targetOrigin, [transfer]);
targetWindow
targetWindow is a reference to the window that receives the message. Methods of obtaining this reference include:
- Window.open
- Window.opener
- HTMLIFrameElement.contentWindow
- Window.parent
- Window.frames + index value
message
The message to be sent to the target window. The data is serialized using a structured cloning algorithm. This means that we can safely pass all kinds of data objects to the target window without having to serialize them ourselves.
targetOrigin
specifies the source of the target window. It must be consistent with the destination of the message. It can be a string or URI. It means that any target window can be received. For the sake of safety, please be sure to specify the recipient’s URI. If so “*”, you can receive it.
transfer
Optional attribute of transfer It is a series messageof Transferableobjects that are passed at the same time . The ownership of these objects will be transferred to the receiver of the message, and the sender will no longer retain ownership.
How to Use postMessage
postMessage program
var receiver = document.getElementById('receiver').contentWindow;
var btn = document.getElementById('send');
btn.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
var val = document.getElementById('text').value;
receiver.postMessage("Hello "+val+"!", "https://znlive.com");
});
How to use js postMessage to transfer messages across domains
Receiving end
window.addEventListener("message", receiveMessage, false);
function receiveMessage(event){
if (event.origin !== "https://znlive.com")
return;
}
How to use js postMessage to transfer messages across domains
eventThe object has three attributes, namely origin, dataand source. event.dataRepresents the received message; event.originRepresents postMessagethe source of sending, including protocol, domain name and port; event.sourceRepresents the reference of the window object that sends the message; We can use this reference to establish two-way communication between two windows from different sources.
Compatibility
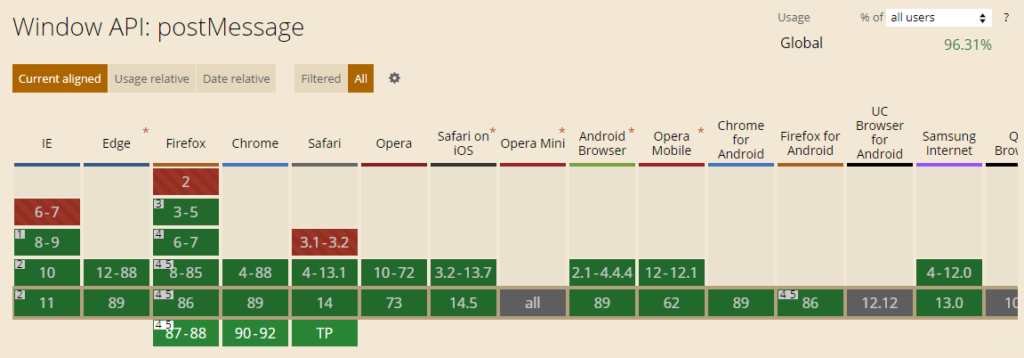
The overall compatibility is still very good!
Application Scenario
- Cross-domain communication (including GET requests and POST requests)
- WebWorker
- The iframe is used in the my project and parameters need to be passed




