Do you know the Linux kernel version number? The Linux kernel version is different, and there is a Linux distribution version. Now the mainstream centos should be centos7. Starting from centos7.2, the kernel version is 3.10, and the later the kernel version is higher.
The higher version of the kernel fixes many bugs of the lower version of the kernel, therefore, the system needs to improve the kernel version, thereby improving security, stability, and adding more functions.

Generally speaking, Linux supports the coexistence of multiple versions of the kernel, which is nothing more than which version of the kernel is applied when the system starts.
Linux kernel version number
There are two types of Linux kernels: official kernels (usually used by kernel developers) and kernels of major Linux distributions (commonly used by general users).
About the Linux kernel version number:
For example:
[root@centos7 ~]# uname -r Linux 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
Do you know the Linux kernel version number
The version number obtained by the query is: 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
- The first group of numbers: 3, the major version number
- The second group of numbers: 10, the minor version number, which is currently a stable version. Generally, an even number means stable, and an odd number means it is in the development version. Usually, this is not used for production.
- Third set of numbers: 0, revision number
- Fourth set of numbers: 1127.19.1, indicating the patch version of the hairstyle version
- el7: It means that the kernel I am using is a dedicated kernel for the RedHat / CentOS series distribution, centos7
- x86_64: An operating system that uses a 64-bit CPU.
Kernel classification
———————————————
Copyright statement: This article is an original article by CSDN blogger “zsk_john” and follows the CC 4.0 BY-SA copyright agreement. Please attach the original source link and this statement for reprinting.
Check the type of kernel on the website: https://www.kernel.org/
Prepatch: Prepatch or “RC” kernels are major kernel pre-releases, primarily aimed at kernel developers and Linux enthusiasts. Must be compiled from source and often contains new features that must be tested before they can be put into a stable release. The Prepatch kernel is maintained and published by Linus Torvalds.
Mainline: The Mainline mainline tree is maintained by Linus Torvalds. This version of the kernel introduces all new features. New Mainline kernels are released every 2-3 months.
Stable: After each mainline kernel is released, it is considered “stable”. Any bug fixes to stable kernels are backtracked from the Mainline tree and used by designated stable kernel maintainers. There are usually only a few bugfix kernel releases until the next mainline kernel is available – unless it’s designated as a “longterm maintenance kernel”. Stable kernel updates are released on demand, usually 2-3 times a month.
Longterm: Usually several “longterm maintenance” kernel releases are provided to fix bugs in older kernels. These kernels only fix major bugs and don’t release releases frequently.
The download address is the official website: as shown below
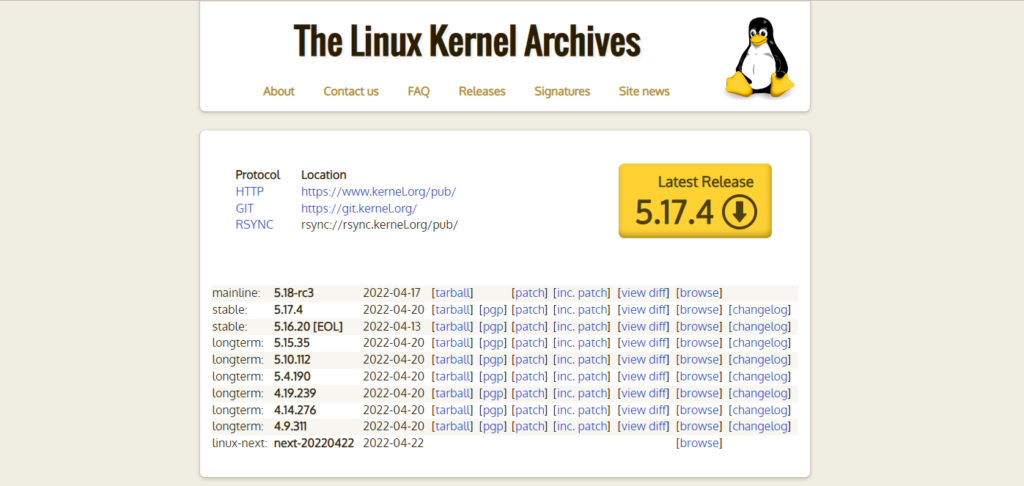
Kernel selection
According to the introduction of the above kernel types, we can know that the stable kernel type and most of the bugs have been fixed are longterm, so you can select a longterm type of kernel in the table in Chapter 2 above. The following experiments are used. 5.4.69 tarball source package.
The reason for the choice is: longterm is a long-term stable version, and most of the bugs have been fixed, the main version is high enough, the kernel is backward compatible, and you can experience more new features.
Kernel upgrade
Usually, centos can coexist with multiple kernels, so it is not recommended to delete the old version of the kernel. After installing the new version of the kernel, grub selects the new version of the kernel to enter the system and use it.
For a more detailed Linux kernel upgrade guide, you can refer to this post.



